Products Categories
| CAS No.: | 71939-50-9 |
|---|---|
| Name: | Dihydroartemisinin |
| Article Data: | 54 |
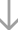
| Molecular Structure: | |
|
|
|
| Formula: | C15H24O5 |
| Molecular Weight: | 284.353 |
| Synonyms: | Cotecxin;DHQHS 2;Dihydroqinghaosu;Salaxin;Santecxin; |
| Density: | 1.24 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point: | 144-149 °C |
| Boiling Point: | 375.6 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point: | 181 °C |
| Appearance: | white solid |
| Safety: | 22-24/25 |
| PSA: | 57.15000 |
| LogP: | 2.18670 |
- 81281-59-67-Benzylideneaminotheophylline
- 82993-81-5D-threo-Ritalinic acid hydrochloride
- 73441-42-6METHYL-5-CHLORO-2,2-DIMETHYLVALERATE
- 852475-26-4MC1568
- 958254-66-51H-Imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine-2-carboxaldehyde, 1-methyl-, hydrochloride
- 99170-93-1N-Methyl-2-oxazolamine
- 914458-26-7[5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-pentyl-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]-1-naphthalenyl-Methanone
- 894852-01-87-BROMO-2,2-DIMETHYL-2H-PYRIDO[3,2-B][1,4]OXAZIN-3(4H)-ONE
- 90221-55-92-bromo-5-methylbenzaldehyde
- 885590-99-82,3-DIFLUORO-4-IODOBENZALDEHYDE

- 63968-64-9
C12H13O2(CH3)3(O)(OO)

- 71939-50-9
dihydroartemisinin

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With methanol; sodium tetrahydroborate at 0℃; for 3h; | 98% |
| With sodium tetrahydroborate In methanol at 0 - 5℃; for 3.33333h; | 97.15% |
| With sodium tetrahydroborate In methanol for 1.25h; | 96% |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With iron(III) chloride In dichloromethane at 25℃; Product distribution; var. temp. and β-arteether/FeCl3 ratios; |

- 255730-31-5
10α-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)-10-deoxoartemisinin

A

- 71939-50-9
dihydroartemisinin

B

- 1093625-96-7
(R)-2-[(3S,4R)-4-Methyl-2-oxo-3-(3-oxo-butyl)-cyclohexyl]-propionaldehyde

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With hemin; L-Cysteine In water; acetonitrile at 23℃; for 24h; pH=7.4; Product distribution; Further Variations:; Reagents; | A 6 % Spectr. B 4 % Spectr. C 6 % Spectr. |


- 85031-59-0, 110715-68-9, 126643-10-5
dihydroartemisinic acid


- 71939-50-9
dihydroartemisinin

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| Multi-step reaction with 2 steps 1: trifluoroacetic acid; oxygen / toluene / -20 - 10 °C / Flow reactor; Photolysis; Irradiation 2: sodium tetrahydroborate; lithium chloride; lithium carbonate; ethanol View Scheme |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With pyridine In dichloromethane at 0 - 20℃; | 100% |
| With pyridine In dichloromethane at 0℃; for 16h; | 100% |
| With pyridine In dichloromethane at 20℃; for 16h; | 97% |

- 71939-50-9
dihydroartemisinin


- 98-88-4
benzoyl chloride


- 163381-14-4
(5aS,6R,8aS,9R,10S,12R,12aR)-3,6,9-trimethyldecahydro-3,12-epoxy[1,2]dioxepino[4,3-i]isochromen-10-yl benzoate

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With pyridine In dichloromethane at 0 - 20℃; for 16h; | 100% |
| With pyridine In dichloromethane at 0℃; for 16h; Inert atmosphere; | 91% |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With pyridine; dmap at 0 - 20℃; for 3h; | 99% |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With dmap In dichloromethane at 20℃; | 98% |
| In pyridine at 20℃; for 8h; | 92% |
| With pyridine; dmap In dichloromethane at 25℃; Acetylation; | 87% |
| With pyridine; dmap at -78 - 20℃; Inert atmosphere; |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With boron trifluoride diethyl etherate In dichloromethane at -10 - -5℃; for 2h; | 97% |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With boron trifluoride diethyl etherate In diethyl ether for 6h; | 96% |
- 6920-22-5DL-1,2-Hexanediol
- 9005-84-9Starch soluble
- 133238-87-62-Butyl-5-nitrobenzofuran
- 389-08-2Nalidixic acid
- 10058-44-3Ferric pyrophosphate
- 1314-06-3Nickel oxide
- 61718-80-71-Pentanone,5-methoxy-1-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-
- 401900-40-1Propanamide,3-[4-(acetylamino)phenoxy]-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-[4-nitro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-,(2S)-
- 104987-11-3Tacrolimus
- 141-53-7Sodium formate
- 8001-54-5Quaternary ammonium compounds, alkylbenzyldimethyl, chlorides
- 9003-39-8Povidone
- 10161-34-9Trenbolone acetate
- 402957-28-2Telaprevir
- 68-19-9Cyanocobalamin
Chemistry
Chemical Name: Dihydroartemisinin
CAS No.: 71939-50-9
Molecular Formula: C15H24O5
Molecular Weight: 284.35 g/mol
Melting Point: 144-149°C
Density: 1.24 g/cm3
Flash Point: 181 °C
Boiling Point: 375.6 °C at 760 mmHg
Storage temp.: 2-8°C
Following is the structure of Dihydroartemisinin (CAS No.:71939-50-9):

Product Categories about Dihydroartemisinin (CAS No.:71939-50-9) are Miscellaneous Natural Products ; Intermediates & Fine Chemicals ; Metabolites & Impurities ; Pharmaceuticals
The chemical synonymous of Dihydroartemisinin (CAS No.:71939-50-9) are (3r,5as,6r,8as,9r,10r,12r,12ar)-Decahydro-3,6,9-trimethyl-3,12-epoxy-12h-pyrano[4,3-j]-1,2-benzodioxepin-10-ol ; Dihydroarteminisin ; Dihydroartemisin ; (3R,5aS,6R,8aS,9R,10S,12R,12aR)-Decahydro-3,6,9-trimethyl- 3,12-epoxy-12H-pyrano[4,3-j]-1,2-benzodioxepin-10-ol ; Alaxin ; b-Dihydroartemisinin ; Cotecxin
Specification
Dihydroartemisinin (CAS No.:71939-50-9) is a drug used to treat malaria. Dihydroartemisinin is the active metabolite of all artemisinin compounds (artemisinin, artesunate, artemether, etc.) and is also available as a drug in itself. The lactone of artemisinin could selectively be reduced with mild hydride-reducing agents, such as sodium borohydride, potassium borohydride, and lithium borohydride to dihydroartemisinin (a lactol) in over 90% yield. It is a novel reduction, because normally lactone cannot be reduced with sodium borohydride under the same reaction conditions. Reduction with LiAlH4 leads to some rearranged products. It was surprising to find that the lactone was reduced, but that the peroxy group survived. However, the lactone of deoxyartemisinin resisted reduction with sodium borohydride and could only be reduced with isobutylaluminium hydride to the lactol, (deoxydihydroartimisinin). These results show that the peroxy group assists the reduction of lactone with sodium borohydride to a lactol, but not to the alcohol which is the over-reduction product. No clear evidence for this reduction process exists.


