Products Categories
| CAS No.: | 1404-90-6 |
|---|---|
| Name: | Vancomycin |
| Article Data: | 8 |
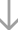
| Molecular Structure: | |
|
|
|
| Formula: | C66H75Cl2N9O24 |
| Molecular Weight: | 1449.27 |
| Synonyms: | 22H-8,11:18,21-Dietheno-23,36-(iminomethano)-13,16:31,35-dimetheno-1H,16H-[1,6,9]oxadiazacyclohexadecino[4,5-m][10,2,16]benzoxadiazacyclotetracosine-26-carboxylicacid, 3-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-44-[[2-O-(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-3-C-methyl-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)-b-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-10,19-dichloro-2,3,4,5,6,7,23,24,25,26,36,37,38,38a-tetradecahydro-7,22,28,30,32-pentahydroxy-6-[[4-methyl-2-(methylamino)-1-oxopentyl]amino]-2,5,24,38,39-pentaoxo-,[3S-[3R*,6S*(S*),7S*,22S*,23R*,26R*,36S*,38aS*]]-;Diatracin;Vancocin;VancocinCP;Vancocine;Vancoled;Vancoplus; |
| EINECS: | 215-772-6 |
| Density: | 1.657 g/cm3 |
| Appearance: | Almost white powder |
| PSA: | 530.49000 |
| LogP: | 4.73460 |
- 144851-82-1METHYL2-AMINO-3-FLUOROBENZOATE
- 483366-12-7(2S,4R)-1-Boc-2-cyano-4-hydroxypyrrolidine
- 173606-50-3BOC-10-AMINODECANOIC ACID
- 361456-36-2METHYL (R)-(+)-ISOCYANATO-3-PHENYLPROPI&
- 5156-58-1N-(1-Benzyl-4-pipperidinyl)-N-phenylpropanamide HCl
- 81281-59-67-Benzylideneaminotheophylline
- 50288-62-5threo-Phenyl-2-piperidyl acetamide
- 82993-81-5D-threo-Ritalinic acid hydrochloride
- 47087-37-6Z-D-Glu-OMe
- 73441-42-6METHYL-5-CHLORO-2,2-DIMETHYLVALERATE

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine; glycosyltransferase GtfD; bovine serum albumin In glycerol at 37℃; for 1.5h; Enzymatic reaction; | 87% |

- 1404-90-6
vancomycin

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With ammonium bicarbonate; palladium on activated charcoal In acetic acid at 23℃; for 4h; Hydrogenolysis; | 81% |
| With ammonium formate; acetic acid; 10percent Pd/C In methanol at 23℃; for 4h; | 81% |

- 216668-88-1
N,N'-dialloc-tri-O-allyl vancomycin allyl ester


- 1404-90-6
vancomycin

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) dichloride; tri-n-butyl-tin hydride In acetic acid; N,N-dimethyl-formamide for 0.166667h; Ambient temperature; | 78% |

A

- 24570-39-6
(R)-2-[(R)-2-((S)-2,6-Bis-acetylamino-hexanoylamino)-propionylamino]-propionic acid

B

- 1404-90-6
vancomycin

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With sodium citrate at 25℃; Equilibrium constant; pH 5.1; |

A

- 1404-90-6
vancomycin

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With sodium citrate at 25℃; Equilibrium constant; pH 5.1; |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With Tris-HCl buffer; N-methyltransferase at 25℃; for 24h; pH=7.5; Methylation; Enzymatic reaction; |


- 1404-90-6
vancomycin

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With lithium hydroxide; water In tetrahydrofuran at 0℃; for 0.333333h; Hydrolysis; |

- 101485-50-1
desvancosaminyl vancomycin


- 755033-86-4
thymidine 5'-(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-3C-methyl-β-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl diphosphate)


- 1404-90-6
vancomycin

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With glycosyltransferase GtfD Enzyme kinetics; Further Variations:; Reagents; |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With sodium hydrogencarbonate In 1,4-dioxane; water | 100% |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With O-(1H-benzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate; N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine In dimethyl sulfoxide; N,N-dimethyl-formamide at 0 - 23℃; | 100% |
- 103-11-72-Ethylhexyl acrylate
- 9001-00-7Bromelain
- 37220-17-0Konjac glucomannan
- 123-63-7Paraldehyde
- 111974-69-7Quetiapine
- 56839-43-11-Propanone,1-(4-ethylphenyl)-2-methyl-3-(1-piperidinyl)-, hydrochloride (1:1)
- 540-69-2Formicacid, ammonium salt (1:1)
- 105-08-81,4-Cyclohexanedimethanol
- 104987-11-3Tacrolimus
- 141-53-7Sodium formate
- 8001-54-5Quaternary ammonium compounds, alkylbenzyldimethyl, chlorides
- 9003-39-8Povidone
- 10161-34-9Trenbolone acetate
- 402957-28-2Telaprevir
- 68-19-9Cyanocobalamin
History
Vancomycin (CAS NO.1404-90-6) was first isolated by EC Kornfeld (working at Eli Lilly) from a soil sample collected from the interior jungles of Borneo by a missionary. The organism that produced it was eventually named Amycolatopsis orientalis.
The compound was initially labelled compound 05865, but was eventually given the generic name, vancomycin (derived from the word "vanquished").In 1958 ,The rapid development of penicillin-resistance by staphylococci led to the compound being fast-tracked for approval by the FDA . Eli Lilly first marketed vancomycin hydrochloride under the trade name Vancocin.
Specification
The Vancomycin, with the CAS registry number 1404-90-6, has the systematic name of (1S,2R,18R,19R,22S,25R,28R,40S)-48-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3-{[(2S,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-22-(2-a mino-2-oxoethyl)-5,15-dichloro-2,18,32,35,37-pentahydroxy-19-{[(2R)-4-methyl-2-(methylamino)pentanoyl]amino}-20,23,26,42,44-pentaoxo-7,13-dioxa-21,24,27,41,43-pentaazaoctacyclo[26.14.2.2~3,6~.2~14,17~ .1~8,12~.1~29,33~.0~10,25~.0~34,39~]pentaconta-3,5,8(48),9,11,14,16,29(45),30,32,34,36,38,46,49-pentadecaene-40-carboxylic acid (non-preferred name).
The physical properties of this chemical are as below: (1)# of Rule of 5 Violations: 3; (2)ACD/BCF (pH 5.5): 1; (3)ACD/BCF (pH 7.4): 1; (4)ACD/KOC (pH 5.5): 1; (5)ACD/KOC (pH 7.4): 1; (6)#H bond acceptors: 33; (7)#H bond donors: 21; (8)#Freely Rotating Bonds: 23; (9)Polar Surface Area: 530.49; (10)Index of Refraction: 1.735; (11)Molar Refractivity: 350.837 cm3; (12)Molar Volume: 874.685 cm3; (13)Polarizability: 139.083×10-24 cm3; (14)Surface Tension: 105.146 dyne/cm; (15)Density: 1.657 g/cm3; (16)Exact Mass: 1447.4302; (17)MonoIsotopic Mass: 1447.4302; (18)Topological Polar Surface Area: 531; (19)Heavy Atom Count: 101; (20)Complexity: 2960.
In addition, you could convert the following datas into the molecular structure:
(1)Canonical SMILES: CC1C(C(CC(O1)OC2C(C(C(OC2OC3=C4C=C5C=C3OC6=C(C=C(C=C6)C(C(C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC5C(=O)NC7C8=CC(=C(C=C8)O)C9=C(C=C(C=C9C(NC(=O)C(C(C1=CC(=C(O4)C=C1)Cl)O)NC7=O)C(=O)O)O) O)CC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC)O)Cl)CO)O)O)(C)N)O
(2)Isomeric SMILES: C[C@H]1[C@H]([C@@](C[C@@H](O1)O[C@@H]2[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O[C@H]2OC3=C4C=C5C=C3OC6=C(C=C(C=C6)[C@H]([C@H](C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)N[C@H]5C(=O)N[C@@H]7C8=CC(=C(C=C8)O)C9=C(C=C(C=C9[C@H](NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C1=CC(=C(O4)C=C1)Cl)O)NC7=O)(=O)O)O)O)CC(=O)N)NC(=O)[C@@H](CC(C)C)NC)O)Cl)CO)O)O)(C)N)O
(3)InChI: InChI=1S/C66H75Cl2N9O24/c1-23(2)12-34(71-5)58(88)76-49-51(83)26-7-10-38(32(67)14- 26)97-40-16-28-17-41(55(40)101-65-56(54(86)53(85)42(22-78)99-65)100-44-21-66(4,70)57(87)24(3)96-44)98-39-11-8-27(15-33(39)68)52(84)50-63(93)75-48(64(94)95)31-18-29(79)19-37(81)45(31)30-13-25(6-9-36(30)80)46(60(90)77-50)74-61(91)47(28)73-59(89)35(20-43(69)82)72-62(49)92/h6-11,13-19,23-24,34-35,42,44,46-54,56-57,65,71,78-81,83-87H,12,20-22,70H2,1-5H3,(H2,69,82)(H,72,92)(H,73,89)(H,74,91)(H,75,93)(H,76,88)(H,77,90)(H,94,95)/t24-,34+,35-,42+,44-,46+,47+,48-,49+,50-,51+,52+,53+,54-,56+,57+,65-,66-/m0/s1
(4)InChIKey: MYPYJXKWCTUITO-LYRMYLQWSA-N
Below are the toxicity information of this chemical:
| Organism | Test Type | Route | Reported Dose (Normalized Dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| infant | TDLo | intravenous | 30mg/kg/20M-C (30mg/kg) | LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: CYANOSIS CARDIAC: OTHER CHANGES | Archives of Disease in Childhood. Vol. 73, Pg. F123, 1995. |
| infant | TDLo | intravenous | 119mg/kg (119mg/kg) | CARDIAC: PULSE RATE INCREASE WITHOUT FALL IN BP VASCULAR: BP LOWERING NOT CHARACTERIZED IN AUTONOMIC SECTION LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: CYANOSIS | Journal of Toxicology, Clinical Toxicology. Vol. 34, Pg. 83, 1996. |
| infant | TDLo | intravenous | 295mg/kg/3D-I (295mg/kg) | KIDNEY, URETER, AND BLADDER: INTERSTITIAL NEPHRITIS | Journal of Toxicology, Clinical Toxicology. Vol. 30, Pg. 285, 1992. |
| man | TDLo | intravenous | 15mg/kg/2H-C (15mg/kg) | VASCULAR: BP ELEVATION NOT CHARACTERIZED IN AUTONOMIC SECTION LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: DYSPNEA | Annals of Pharmacotherpy. Vol. 33, Pg. 1043, 1999. |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 1734mg/kg (1734mg/kg) | "Index of Antibiotics from Actinomycetes," Umezawa, H. et al., eds., Tokyo, Univ. of Tokyo Press, 1967Vol. -, Pg. 675, 1967. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intravenous | 430mg/kg (430mg/kg) | Journal of Antibiotics. Vol. 43, Pg. 913, 1990. | |
| mouse | LD50 | subcutaneous | 5gm/kg (5000mg/kg) | "CRC Handbook of Antibiotic Compounds," Vols.1- , Berdy, J., Boca Raton, FL, CRC Press, 1980Vol. 1, Pg. 315, 1980. | |
| women | TDLo | intravenous | 15mg/kg/90M-C (15mg/kg) | SKIN AND APPENDAGES (SKIN): "DERMATITIS, ALLERGIC: AFTER SYSTEMIC EXPOSURE" | New England Journal of Medicine. Vol. 313, Pg. 756, 1985. |
| women | TDLo | intravenous | 170mg/kg/19D- (170mg/kg) | BLOOD: AGRANULOCYTOSIS | Canadian Medical Association Journal. Vol. 132, Pg. 39, 1985. |
| women | TDLo | multiple routes | 30mg/kg/2D-I (30mg/kg) | SKIN AND APPENDAGES (SKIN): "DERMATITIS, OTHER: AFTER SYSTEMIC EXPOSURE" | Annals of Internal Medicine. Vol. 115, Pg. 410, 1991. |

