Products Categories
| CAS No.: | 8025-81-8 |
|---|---|
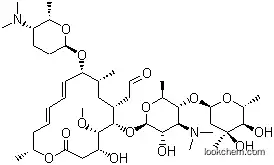
| Name: | Spiramycin |
| Molecular Structure: | |
 |
|
| Formula: | C43H74N2O14 |
| Molecular Weight: | 843.06 |
| Synonyms: | Spiramycine [INN-French];Foromacidin;Sequamycin;5337 R.P.;Spiramycinum [INN-Latin];Antibiotic 799;78355-64-3;Provamycin;Espiramicina [INN-Spanish];Rovamycin;2-[(2R,4E,6E,8R,9R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-12-[5-(4,5-dihydroxy-4,6-dimethyl-oxan-2-yl)oxy-4-dimethylamino-3-hydroxy-6-methyl-oxan-2-yl]oxy-8-(5-dimethylamino-6-methyl-oxan-2-yl)oxy-14-hydroxy-13-methoxy-2,9-dimethyl-16-oxo-1-oxacyclohexadeca-4,6-dien-11-yl]acetaldehyde;Espiramicin;Prestwick_121;1394-00-9;Spiramycin [USAN:BAN:INN];5337R.P.;ROVAMICINA;Spiramycin Base;NSC-64393;SELECTOMYCIN;SPIRAMYCINS;Kitasamycin Premix 10%, 50%;Espiramicina; |
| EINECS: | 232-429-6 |
| Density: | 1.217 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point: | 126-128 °C |
| Boiling Point: | 913.679 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point: | 506.375 °C |
| Solubility: | ethanol: 50 mg/mL, clear to slightly hazy, light-yellow |
| Appearance: | white or slightly yellowish powder |
| Hazard Symbols: |
 Xi Xi
|
| Risk Codes: | 36/37/38 |
| Safety: | 26-36 |
| PSA: | 0.00000 |
| LogP: | 0.00000 |
- 81281-59-67-Benzylideneaminotheophylline
- 82993-81-5D-threo-Ritalinic acid hydrochloride
- 852475-26-4MC1568
- 958254-66-51H-Imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine-2-carboxaldehyde, 1-methyl-, hydrochloride
- 99170-93-1N-Methyl-2-oxazolamine
- 914458-26-7[5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-pentyl-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]-1-naphthalenyl-Methanone
- 894852-01-87-BROMO-2,2-DIMETHYL-2H-PYRIDO[3,2-B][1,4]OXAZIN-3(4H)-ONE
- 90221-55-92-bromo-5-methylbenzaldehyde
- 885590-99-82,3-DIFLUORO-4-IODOBENZALDEHYDE
- 97730-31-9(S)-4'-(2-Methylbutyl)Biphenyl-4-Carbonitrile
- 53-36-1Methylprednisolone acetate
- 103890-78-4Lacidipine
- 50-44-26-Mercaptopurine
- 26921-17-5(S)-Timolol maleate
- 60628-96-81H-Imidazole,1-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-ylphenylmethyl)-
- 78-96-62-Propanol,1-amino-
- 10380-28-6Copper quinolate
- 609-08-5Propanedioicacid, 2-methyl-, 1,3-diethyl ester
- 104987-11-3Tacrolimus
- 141-53-7Sodium formate
- 8001-54-5Quaternary ammonium compounds, alkylbenzyldimethyl, chlorides
- 9003-39-8Povidone
- 10161-34-9Trenbolone acetate
- 402957-28-2Telaprevir
- 68-19-9Cyanocobalamin
Consensus Reports
Specification
The Spiramycin, with the CAS registry number 8025-81-8, is also known as Foromacidin. It belongs to the product categories of Miscellaneous Natural Products; Antibacterial; Antibiotics for Research and Experimental Use; Biochemistry; Macrolides (Antibiotics for Research and Experimental Use); Macrolides; Macrolides Antibiotics; MLSAlphabetic; SN - SZMore...Close...; Antibiotics; Antibiotics A to; Antibiotics N-SAntibiotics; Bactericidal Antibiotics; Chemical Structure; Chemical Structure Class; Interferes with Protein Synthesis Spectrum of Activity; L - ZAntibiotics; Mechanism of Action; Principle; S; Peptide Synthesis/Antibiotics. Its EINECS registry number is 232-429-6. This chemical's molecular formula is C43H74N2O14 and molecular weight is 785.96. What's more, both its IUPAC name and systematic name are the same which is called 2-[(4R,5S,6S,7R,9R,10R,11E,13E,16R)-6-[5-(4,5-Dihydroxy-4,6-dimethyloxan-2-yl)oxy-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-10-[5-(dimethylamino)-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-9,16-dimethyl-2-oxo-1-oxacyclohexadeca-11,13-dien-7-yl]acetaldehyde. Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic. It is used to treat toxoplasmosis and various other infections of soft tissues.
Physical properties about Spiramycin are: (1)ACD/LogP: 2.745; (2)# of Rule of 5 Violations: 2; (3)ACD/LogD (pH 5.5): -1.24; (4)ACD/LogD (pH 7.4): 1.26; (5)ACD/BCF (pH 5.5): 1.00; (6)ACD/BCF (pH 7.4): 2.34; (7)ACD/KOC (pH 5.5): 1.00; (8)ACD/KOC (pH 7.4): 24.12; (9)#H bond acceptors: 16; (10)#H bond donors: 4; (11)#Freely Rotating Bonds: 15; (12)Polar Surface Area: 195.38 Å2; (13)Index of Refraction: 1.55; (14)Molar Refractivity: 220.711 cm3; (15)Molar Volume: 692.831 cm3; (16)Polarizability: 87.497×10-24 cm3; (17)Surface Tension: 52.75 dyne/cm; (18)Density: 1.217 g/cm3; (19)Flash Point: 506.375 °C; (20)Enthalpy of Vaporization: 150.806 kJ/mol; (21)Boiling Point: 913.679 °C at 760 mmHg; (22)Vapour Pressure: 0 mmHg at 25 °C.
When you are dealing with this chemical, you should be very careful. This chemical is inflammation to the skin, eyes and respiratory system or other mucous membranes. Therefore, you should wear suitable protective clothing. In case of contacting with eyes, you should rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
You can still convert the following datas into molecular structure:
(1) SMILES: O=CC[C@@H]4[C@H](OC2OC(C(OC1OC(C)C(O)C(O)(C)C1)C(N(C)C)C2O)C)[C@@H](OC)[C@H](O)CC(=O)O[C@H](C)C\C=C\C=C\[C@H](OC3OC(C)C(N(C)C)CC3)[C@H](C)C4
(2) InChI: InChI=1S/C43H74N2O14/c1-24-21-29(19-20-46)39(59-42-37(49)36(45(9)10)38(27(4)56-42)58-35-23-43(6,51)41(50)28(5)55-35)40(52-11)31(47)22-33(48)53-25(2)15-13-12-14-16-32(24)57-34-18-17-30(44(7)8)26(3)54-34/h12-14,16,20,24-32,34-42,47,49-51H,15,17-19,21-23H2,1-11H3/b13-12+,16-14+/t24-,25-,26?,27?,28?,29+,30?,31-,32+,34?,35?,36?,37?,38?,39+,40+,41?,42?,43?/m1/s1
(3) InChIKey: ACTOXUHEUCPTEW-JMRHEKERSA-N
The toxicity data is as follows:
| Organism | Test Type | Route | Reported Dose (Normalized Dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dog | LD50 | oral | 5200mg/kg (5200mg/kg) | Canadian Medical Association Journal. Vol. 77, Pg. 623, 1957. | |
| dog | LD50 | oral | 5200mg/kg (5200mg/kg) | GASTROINTESTINAL: NAUSEA OR VOMITING BEHAVIORAL: ALTERED SLEEP TIME (INCLUDING CHANGE IN RIGHTING REFLEX) | Canadian Medical Association Journal. Vol. 77, Pg. 623, 1957. |
| man | TDLo | oral | 133mg/kg/5D (133mg/kg) | GASTROINTESTINAL: "HYPERMOTILITY, DIARRHEA" GASTROINTESTINAL: OTHER CHANGES | Lancet. Vol. 2, Pg. 993, 1978. |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 322mg/kg (322mg/kg) | Japanese Journal of Antibiotics. Vol. 23, Pg. 429, 1970. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intravenous | 130mg/kg (130mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 8, Pg. 386, 1958. | |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | 2900mg/kg (2900mg/kg) | Therapie. Vol. 23, Pg. 161, 1968. | |
| mouse | LD50 | subcutaneous | 1470mg/kg (1470mg/kg) | Japanese Journal of Antibiotics. Vol. 23, Pg. 429, 1970. | |
| mouse | LDLo | unreported | 100mg/kg (100mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 17, Pg. 693, 1967. | |
| rabbit | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 1130mg/kg (1130mg/kg) | Japanese Journal of Antibiotics. Vol. 23, Pg. 429, 1970. | |
| rabbit | LD50 | intravenous | 182mg/kg (182mg/kg) | Japanese Journal of Antibiotics. Vol. 23, Pg. 429, 1970. | |
| rabbit | LD50 | oral | > 4gm/kg (4000mg/kg) | Japanese Journal of Antibiotics. Vol. 23, Pg. 429, 1970. | |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 575mg/kg (575mg/kg) | Japanese Journal of Antibiotics. Vol. 23, Pg. 429, 1970. | |
| rat | LD50 | intravenous | 170mg/kg (170mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 8, Pg. 386, 1958. | |
| rat | LD50 | oral | 3550mg/kg (3550mg/kg) | Japanese Journal of Antibiotics. Vol. 23, Pg. 429, 1970. | |
| rat | LD50 | subcutaneous | 1gm/kg (1000mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 8, Pg. 386, 1958. |

